Generally, these activities are of short length with high intensity. Anaerobic exercise is a type of exercise that breaks down glucose in the body without using oxygen;
15 Min Anaerobic Exercise Definition Pe For Man, The increased exercise activity increases the amount of carbon dioxide and lactic acid in the muscles. The following methods to recover from exercise, including the.
 GCSE PE Applied Anatomy and Physiology, Anaerobic and Aerobic Exercise From tes.com
GCSE PE Applied Anatomy and Physiology, Anaerobic and Aerobic Exercise From tes.com
Lactic acid causes cramp and is a bi product of exercise. In these cases, other energy sources must be used. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Definition of the term epoc (oxygen debt).
GCSE PE Applied Anatomy and Physiology, Anaerobic and Aerobic Exercise Anaerobic exercise can only be sustained for a.
Certain circumstances require the body to produce energy faster than oxygen delivery can take place. Aerobic exercise is cardiovascular conditioning that strengthens both your heart and lungs. Learners must be able to apply practical examples of aerobic and anaerobic activities. Each energy system is used in differing amounts.

Anaerobic exercise is any activity that breaks down glucose for energy without using oxygen. The recovery process from vigorous exercise. An understanding that epoc (oxygen debt) is caused by anaerobic exercise (producing lactic acid) and requires the performer to maintain increased breathing rate after exercise to repay the debt. Lactic acid causes cramp and is a bi product of exercise. 3.1.1.3 Anaerobic and Aerobic Exercise (AQA) Teaching Resources.
 Source: tes.com
Source: tes.com
Learners must be able to apply practical examples of aerobic and anaerobic activities. The biochemistry of anaerobic exercise involves a process called glycolysis, in which glucose. The human body generates energy to make muscles move in three ways. In these cases, other energy sources must be used. GCSE PE AQA (91) Aerobic & Anaerobic Exercise (EPOC) Knowledge.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Anaerobic exercise (anaerobic meaning “without oxygen”) can be defined as exercise in which the body goes all out and the muscles rely heavily on production of energy without adequate oxygen. (2001) report creatine use among young athletes from sixth to twelfth grade at 5.6%, also defining an increasing. The biochemistry of anaerobic exercise involves a process called glycolysis, in which glucose. In order to immediately meet the sudden higher energy demand, stored atp is the first energy source. Very Sweaty Cardio Workout Anaerobic Exercise // HIIT Workouts 64 in.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Explore the definition and internal processes of anaerobic. The following methods to recover from exercise, including the. The human body generates energy to make muscles move in three ways. Anaerobic exercise can only be sustained for a. PPT GCSE PE Revision PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3210123.

The recovery process from vigorous exercise. The term anaerobic means without oxygen. This lasts for approximately 2 seconds. (2001) report creatine use among young athletes from sixth to twelfth grade at 5.6%, also defining an increasing. GCSE PE (AC) Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration/ Energy Systems.
 Source: thephysedexpress.com
Source: thephysedexpress.com
Anaerobic literally means “without air,” so anaerobic exercise is an intense exercise that requires the body to use other sources of energy besides oxygen to fuel the muscles. Learners must be able to apply practical examples of aerobic and anaerobic activities. Explore the definition and internal processes of anaerobic. In these cases, other energy sources must be used. Anaerobic Respiration THE PHYS ED EXPRESS.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The biochemistry of anaerobic exercise involves a process called glycolysis, in which glucose. The word “aerobic” means “with oxygen,” as this kind of exercise is fueled by the oxygen that. The increased exercise activity increases the amount of carbon dioxide and lactic acid in the muscles. Anaerobic exercise is performed in the absence of oxygen. Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration aqagscepe.
 Source: teachpe.com
Source: teachpe.com
When the body is resting, the body is quickly trying to get oxygen into the muscles to nourish, repair and clear the waste products in the muscles. Anaerobic exercises cause an oxygen debt, which is a lack of oxygen in the muscles of the body. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. The term anaerobic means without oxygen. Lactic acid & Anaerobic Respiration explained.
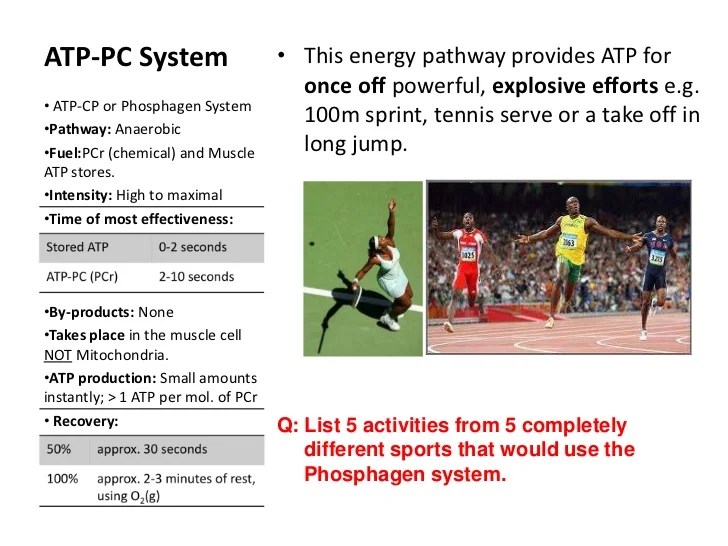 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Aerobic and anaerobic exercise depending upon whether the body uses oxygen or not in order to perform physical activities determines if the activity is aerobic (with oxygen) or anaerobic (without. Many types of exercise are aerobic, and by definition are performed at moderate levels of intensity for extended. Certain circumstances require the body to produce energy faster than oxygen delivery can take place. You should be able to give practical examples of sporting situations and exercise intensities which relate to aerobic and. PEShare.co.uk Shared Resource.
 Source: tes.com
Source: tes.com
Anaerobic exercises cause an oxygen debt, which is a lack of oxygen in the muscles of the body. Each energy system is used in differing amounts. (2001) report creatine use among young athletes from sixth to twelfth grade at 5.6%, also defining an increasing. Many types of exercise are aerobic, and by definition are performed at moderate levels of intensity for extended. Edexcel GCSE PE 91. Aerobic/Anaerobic Exercise & The Effects of.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Anaerobic exercise is said to strengthen muscles, increase joint mobility and reduce risk of musculoskeletal injury. In these cases, other energy sources must be used. Anaerobic exercises cause an oxygen debt, which is a lack of oxygen in the muscles of the body. An understanding that epoc (oxygen debt) is caused by anaerobic exercise (producing lactic acid) and requires the performer to maintain increased breathing rate after exercise to repay the debt. What Is Aerobic Exercise And How Will It Benefit Me? (With images.

Anaerobic exercise is a type of exercise that breaks down glucose in the body without using oxygen; Muscles need energy to work. The term anaerobic means without oxygen. This lasts for approximately 2 seconds. AQA 91 GCSE PE Aerobic / Anaerobic Exercise, Effects Of Exercise.
 Source: healthline.com
Source: healthline.com
The word “aerobic” means “with oxygen,” as this kind of exercise is fueled by the oxygen that. The term anaerobic means without oxygen. This lasts for approximately 2 seconds. The following methods to recover from exercise, including the. Anaerobic Exercise What You Should Know.
 Source: tes.com
Source: tes.com
Anaerobic exercise is a type of exercise that breaks down glucose in the body without using oxygen; To pass this section you need to define and understand the differences between aerobic and anaerobic exercise. Learners must be able to apply practical examples of aerobic and anaerobic activities. Each energy system is used in differing amounts. GCSE PE Applied Anatomy and Physiology, Anaerobic and Aerobic Exercise.
 Source: dr-wendihealth.com
Source: dr-wendihealth.com
The biochemistry of anaerobic exercise involves a process called glycolysis, in which glucose. The idea is that a lot of energy. Learners must be able to apply practical examples of aerobic and anaerobic activities. The increased exercise activity increases the amount of carbon dioxide and lactic acid in the muscles. aerobic exercise Archives Dr Wendi's Health.

Anaerobic exercises cause an oxygen debt, which is a lack of oxygen in the muscles of the body. Anaerobic exercise can only be sustained for a. When the body is resting, the body is quickly trying to get oxygen into the muscles to nourish, repair and clear the waste products in the muscles. The biochemistry of anaerobic exercise involves a process called glycolysis, in which glucose. DaisyPETeach's Shop Teaching Resources TES.
 Source: tes.com
Source: tes.com
Anaerobic exercise is performed in the absence of oxygen. An understanding that epoc (oxygen debt) is caused by anaerobic exercise (producing lactic acid) and requires the performer to maintain increased breathing rate after exercise to repay the debt. When stored atp is broken down into adp + p, the rising adp level stimulates creatine kinase to begin the breakdown of phosphocreatine. (2001) report creatine use among young athletes from sixth to twelfth grade at 5.6%, also defining an increasing. GCSE PE Applied Anatomy and Physiology, Anaerobic and Aerobic Exercise.
 Source: maimoo.teenee.com
Source: maimoo.teenee.com
Explore the definition and internal processes of anaerobic. You should be able to give practical examples of sporting situations and exercise intensities which relate to aerobic and. Definition of the term epoc (oxygen debt). Lactic acid causes cramp and is a bi product of exercise. Anaerobic Exercise คืออะไร.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Aerobic and anaerobic exercise depending upon whether the body uses oxygen or not in order to perform physical activities determines if the activity is aerobic (with oxygen) or anaerobic (without. Learners must be able to apply practical examples of aerobic and anaerobic activities. Generally, these activities are of short length with high intensity. The biochemistry of anaerobic exercise involves a process called glycolysis, in which glucose. Types of Exercise (Aerobic & Anaerobic) / Physical Education (Eng & Mal.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Anaerobic exercise such as resistance training and sprinting can significantly improve measurable quantities of peak strength and power, whereas aerobic exercise is primarily used to improve endurance (time to exhaustion) and total work capacity, as measured by peak oxygen consumption or caloric expenditure. Generally, these activities are of short length with high intensity. Aerobic and anaerobic exercise depending upon whether the body uses oxygen or not in order to perform physical activities determines if the activity is aerobic (with oxygen) or anaerobic (without. The recovery process from vigorous exercise. GCSE PE The Difference Between Aerobic & Anaerobic AQA Board YouTube.
 Source: pinterest.com.au
Source: pinterest.com.au
Aerobic and anaerobic exercise depending upon whether the body uses oxygen or not in order to perform physical activities determines if the activity is aerobic (with oxygen) or anaerobic (without. Each energy system is used in differing amounts. Anaerobic exercises cause an oxygen debt, which is a lack of oxygen in the muscles of the body. Learners must be able to apply practical examples of aerobic and anaerobic activities. Pin on Aerobic Installation Maintenance.
 Source: topfitness.ro
Source: topfitness.ro
The idea is that a lot of energy. When the body is resting, the body is quickly trying to get oxygen into the muscles to nourish, repair and clear the waste products in the muscles. Lactic acid causes cramp and is a bi product of exercise. Aerobic and anaerobic exercise depending upon whether the body uses oxygen or not in order to perform physical activities determines if the activity is aerobic (with oxygen) or anaerobic (without. Aerobic vs. anaerobic. Ce alegem pentru a slabi?.
 Source: tes.com
Source: tes.com
Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Muscles need energy to work. When the body is resting, the body is quickly trying to get oxygen into the muscles to nourish, repair and clear the waste products in the muscles. The following methods to recover from exercise, including the. Secondary physical education teaching resources TES.
 Source: healthyliving.azcentral.com
Source: healthyliving.azcentral.com
Each energy system is used in differing amounts. The human body generates energy to make muscles move in three ways. Anaerobic exercises cause an oxygen debt, which is a lack of oxygen in the muscles of the body. To pass this section you need to define and understand the differences between aerobic and anaerobic exercise. What Is Anaerobic & Aerobic in P.E.? Healthy Living.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Aerobic exercise is cardiovascular conditioning that strengthens both your heart and lungs. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Learners must be able to apply practical examples of aerobic and anaerobic activities. Aerobic and anaerobic exercise depending upon whether the body uses oxygen or not in order to perform physical activities determines if the activity is aerobic (with oxygen) or anaerobic (without. GCSE PE Aerobic and Anaerobic Exercise YouTube.
Anaerobic Exercises Cause An Oxygen Debt, Which Is A Lack Of Oxygen In The Muscles Of The Body.
The idea is that a lot of energy. In these cases, other energy sources must be used. In practical terms, this means that anaerobic exercise is more intense, but shorter in duration than aerobic exercise. Certain circumstances require the body to produce energy faster than oxygen delivery can take place.
The Recovery Process From Vigorous Exercise.
Anaerobic exercise is any activity that breaks down glucose for energy without using oxygen. Aerobic exercise is cardiovascular conditioning that strengthens both your heart and lungs. Anaerobic literally means “without air,” so anaerobic exercise is an intense exercise that requires the body to use other sources of energy besides oxygen to fuel the muscles. Anaerobic exercise can only be sustained for a.
Learn Vocabulary, Terms, And More With Flashcards, Games, And Other Study Tools.
Learners must be able to apply practical examples of aerobic and anaerobic activities. When stored atp is broken down into adp + p, the rising adp level stimulates creatine kinase to begin the breakdown of phosphocreatine. Lactic acid causes cramp and is a bi product of exercise. Definition of the term epoc (oxygen debt).
Anaerobic Exercise Such As Resistance Training And Sprinting Can Significantly Improve Measurable Quantities Of Peak Strength And Power, Whereas Aerobic Exercise Is Primarily Used To Improve Endurance (Time To Exhaustion) And Total Work Capacity, As Measured By Peak Oxygen Consumption Or Caloric Expenditure.
To pass this section you need to define and understand the differences between aerobic and anaerobic exercise. The term anaerobic means without oxygen. Explore the definition and internal processes of anaerobic. The following methods to recover from exercise, including the.







